15 SEO Myths and Misconceptions
Keep clear of these things
There’s a lot of information about what SEO actually IS, but what about what it ISN’T?
Welcome to the world of SEO myths. These can lead you to waste precious time and money on things that will never improve SEO. Here are my top 15 common SEO myths and misconceptions.
Search Engine Optimisation is an essential part of marketing strategy. If you want to get noticed by potential customers, you should invest some budget into this part of digital marketing. There are many myths surrounding the SEO industry, here are a few explained.
- SEO is a one-time job
- SEO is dead
- PPC advertising helps rankings
- There is a duplicate content penalty
- Domain age is a ranking factor
- Google cares about Domain Authority
- LSI keywords improve your rankings
- Bounce Rate is a ranking factor
- You cannot rank a slow-loading page
- Buying 20,000 backlinks for £10 works
- Quantity of links is more important than quality
- Social signals are a ranking factor
- Google uses Google analytics data for rankings
- XML sitemaps boost rankings
- SEO is extremely expensive
Common SEO Misconceptions broken down
1 - SEO is a one-time job
Many people think that once you’ve got a site built and running, you’re done and don’t have to worry about it anymore. They believe that once they’ve “done their part,” there’s nothing else to do except sit back and wait for their search rankings to grow. This couldn’t be further from the truth. In fact, most businesses are still struggling to understand how to use SEO effectively.
The news is that SEO isn’t a one-time deal and it tends not to be something your IT department or Developer can do. You’ll always want to keep tweaking your efforts to ensure that you’re keeping up with changes in search algorithms and best practices. However, it doesn’t mean that you have to start over every single day. There are plenty of things that you can manage to improve your rankings without having to completely rebuild everything.
2 - SEO is dead
This myth appears every time Google launches an algorithmic change. For example, it happened in April 2017 when Google launched Hummingbird. In response to the update, many people claimed that SEO was dead. They said that there was no longer a place for SEO because Google had changed everything about how search works. People believed that Google was doing away with keywords, meta tags, and even the way that they rank sites.
In fact, nothing could be further from the truth. There are still plenty of opportunities for SEO. However, what we do needs to adapt to Google’s ever-changing algorithms. We need to make sure that our strategies remain relevant. If we don’t, we risk losing out on traffic and revenue.
The truth is that SEO isn’t dead. It just needs to evolve. As long as you understand the parts that are ever-changing SEO and work with someone who knows how to apply those techniques effectively, you can still succeed.
3 - PPC advertising helps rankings
Many people believe that running paid search campaigns through Google AdWords help rankings. While there are some benefits to having a strong presence in the paid search space, there are no direct effects on rankings.
Google’s algorithm for ranking organic results is completely separate from how it determines where ads are displayed.
It’s possible you could see an uplift in organic traffic because people see your Ads and remember the company name/site but just giving Google cash via PPC does not improve your organic rankings.
4 - There is a duplicate content penalty
This is one of the biggest myths about SEO. Many people think that if your content is duplicated across multiple URLs, it will hurt your rankings. However, there are actually many reasons why this isn’t true. First off, there is no penalty for having duplicate content. Secondly, even if you do have duplicate content, it doesn’t necessarily mean that it will cause penalties. In fact, duplicate content does not always affect your rankings negatively.
However, if you want to avoid penalisation, you must make sure that each URL contains unique information. You cannot use one URL to host different versions of your content because Google will see that as duplicate content. Also, don’t forget to keep track of how much time you spend creating content. If you find yourself spending too much time writing, editing, and promoting content, you might consider outsourcing some of those tasks.
5 - Domain age is a ranking factor
Only even slightly true in that an older site/domain may have more quality backlinks but there’s nothing to stop a brand new domain ranking well if it has great content and delivers a good user experience. Besides, if domain age mattered that much how do new sites disrupt an established part of the search results? (think Uber and/or AirBnb here – even Amazon)
6 - Google uses Domain Authority for rankings
Domain Authority – often referred to as just ‘DA’ is a third party metric developed by Moz (a leading provider of SEO tools) with the aim of providing some kind of measurement that approximates to PageRank (which is a Google metric which was developed during their early days). DA has no part in Google’s algorithms whatsoever. Sure, increasing your DA (via good links) may well help your organic rankings, but this is just good practice SEO and not DA at work.
7 - LSI keywords improve your rankings
This acronym stands for Latent Semantic Indexing and relates to similar terms around a page’s content to help search engines understand the topic. The thing is, they don’t exist, at least not as an SEO factor. Adding more information around a topic in order to better serve the search query and intent is a great thing to do, but if someone offers to add LSI keywords as part of their service, run a mile. Here’s what Google’s John Mueller has to say about it:
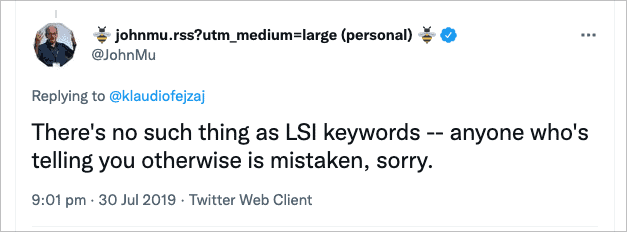
Don’t mistake LSI with ‘long-tail keywords’ – these are more relevant keywords and are a good thing to employ across your content.
A bonus one here is keyword density – which seems to think x% of your keywords need to be in each paragraph. That’s from 2005!
8 - Bounce Rate is a ranking factor
The concept of bounce rate being a ranking factor is nothing new. However, there has never been enough evidence to prove that bounce rates affect rankings. So what is it about bounce rate that makes some people think it is important?
There are several reasons why some believe that bounce rate affects rankings. One reason is that bounce rate appears in many Analytics tools. Another reason is that some people say that bounce rate is a better indicator of quality than average position. A third reason is that some people argue that bounce rate is a metric that indicates how long someone stays on a particular page.
However, none of those three reasons actually proves that bounce rate is a factor in Google’s algorithm. To understand why we must look at the definition of bounce rate.
What Is Bounce Rate?
A bounce occurs when a person lands on a page and leaves immediately. This could happen for a number of different reasons. For example, the person may have found exactly what he/she wanted on the page – think of your contact page here for instance.
9 - You cannot rank a slow loading page
We all like a fast website and if you work with me I will definitely check your page speed and recommend changes to help improve this. However, you could have the fastest website in the world that is a) hard to navigate, b) is full of low-quality ‘thin’ content and c) is hard for search engines to crawl – and it will rank badly. There’s a saying of “fast crap is still crap” so look at content and user experience before obsessing too much over how fast things are. There are 000s of slow sites out there ranking well for very competitive terms.
10 - Buying 20,000 backlinks for £10 works
Google has announced many times it had updated its algorithms to combat “link buying,” where companies buy large amounts of links to boost rankings. The update included penalties for purchasing links from poor quality sources. (look up Panda in the history of major Google updates for more).
Buying links from generic, spyware-ridden directories, link farms or unprofessional webmasters will put your site on the fast track to penalty. These types of links are often bought by people trying to game the system, and there are many ways to identify such links. Google wants you to earn links naturally, from reputable sources.
Now, thousands and thousands of suspicious links will do more harm to your site than good. A study found that having one hundred thousand links pointing to your site from low-quality sources will hurt your reputation more than having ten million high-quality links.
Google is fighting back against suspect links, and now, thousands and thousands of links will actually hurt your site more than help it. If you want to keep your site safe from penalty, focus on earning links from trusted sources. You can ask customers or partners for a link, or try to build relationships with other businesses in your industry.
11 - Quantity of links is more important than quality
Backlinks are one of the most important factors used to determine how authoritative a site is. They’re often considered the “vote of confidence” for your site. If you’ve ever wondered whether having more backlinks makes you look better, you might want to think again.
The truth about backlinks is that they aren’t just votes for your site; they’re votes for the sites linking to yours. Some studies show that even though backlinks do matter, they don’t always count as much as we’d like to believe. For example, research conducted by Moz found that out of 10,000 different websites, only 11% had more than 500 backlinks. But those same websites received almost 70% of the total traffic.
So what does this mean for us? Well, it means that if you’re trying to gain recognition for yourself, you should focus on building relationships with reputable sources rather than looking for ways to increase your backlinks. Doing so could actually hurt your reputation.
12 - Social signals are a ranking factor
In 2010, Google CEO Eric Schmidt told TechCrunch that “social signals are not a ranking factor,” adding that “Google doesn’t care what you do on Facebook.” He added that “we don’t want to know how many people follow you on Twitter… we just want to find things that matter.”
Fast forward to today, where every single blog post about social signals seems to be written by someone who wants to sell something. They’re either trying to convince clients that they need to buy some sort of tool to improve their rankings, or they’re selling themselves as consultants. Either way, they’re wrong.
The fact that Google has changed its tune over the years says nothing good about those who continue to believe otherwise.
13 - Google uses Google analytics data for rankings
Google doesn’t use data from Google Analytics to determine search rankings. In fact, it won’t even tell you which keywords land your site via search engines. But there might be a way to figure out how much traffic you’re getting from Google searches. And we know that Google does track some information about how often people come to your site, but it isn’t used to rank sites.
The reason why is pretty simple: Google wants to keep things fair. If they could easily see what sites were doing well, then they would be able to game the system. So, no, Google Analytics data isn’t being used to rank sites. Besides, not every site uses Google Analytics – there are many other Analytics tools out there – what about those?
14 - XML sitemaps boost rankings
No, they don’t – these are not ranking signals. XML sitemaps are a special kind of file that search engines read to discover pages and fresh content on your site. For large sites, these are a must, for smaller sites a clear menu and navigation, plus the use of internal links, is enough to get your pages found. Please also don’t submit your sitemaps to search engines all the time/manually – this is a waste. If they know about your sitemap file(s), they will check back on them often.
15 - SEO is extremely expensive
The idea that SEO is expensive is a common misconception. In fact, it’s just the opposite. There are many different types of SEO packages out there, ranging from basic to premium. And while some companies charge thousands of pounds per month, others offer affordable solutions for those looking to grow their brand via organic search.
An SEO service can be tailored around your specific needs and goals. For example, a small business might want to rank high on local searches without spending too much money. On the other hand, a large corporation might require a complete overhaul of its site and a lot of work to optimise certain areas.
Regardless of how big or small your company is, there is an affordable solution for every budget.
So there you have it
If you want a proper SEO strategy with good old-fashioned service for your business, please get in touch.
Talk To Dan